- 没有索引或者没有用到索引(这是查询慢最常见的问题,是程序设计的缺陷)
- I/O吞吐量小,形成了瓶颈效应。
- 没有创建计算列导致查询不优化。
- 内存不足
- 网络速度慢
- 查询出的数据量过大(可以采用多次查询,其他的方法降低数据量)
- 锁或者死锁(这也是查询慢最常见的问题,是程序设计的缺陷)
- sp_lock,sp_who,活动的用户查看,原因是读写竞争资源。
- 返回了不必要的行和列
- 查询语句不好,没有优化
SQL Server T-SQL Samples
Ø 基本常用查询
--select
select * from student;
--all 查询所有
select all sex from student;
--distinct 过滤重复
select distinct sex from student;
--count 统计
select count(*) from student;
select count(sex) from student;
select count(distinct sex) from student;
--top 取前N条记录
select top 3 * from student;
--alias column name 列重命名
select id as 编号, name '名称', sex 性别 from student;
--alias table name 表重命名
select id, name, s.id, s.name from student s;
--column 列运算
select (age + id) col from student;
select s.name + '-' + c.name from classes c, student s where s.cid = c.id;
--where 条件
select * from student where id = 2;
select * from student where id > 7;
select * from student where id < 3;
select * from student where id <> 3;
select * from student where id >= 3;
select * from student where id <= 5;
select * from student where id !> 3;
select * from student where id !< 5;
--and 并且
select * from student where id > 2 and sex = 1;
--or 或者
select * from student where id = 2 or sex = 1;
--between ... and ... 相当于并且
select * from student where id between 2 and 5;
select * from student where id not between 2 and 5;
--like 模糊查询
select * from student where name like '%a%';
select * from student where name like '%[a][o]%';
select * from student where name not like '%a%';
select * from student where name like 'ja%';
select * from student where name not like '%[j,n]%';
select * from student where name like '%[j,n,a]%';
select * from student where name like '%[^ja,as,on]%';
select * from student where name like '%[ja_on]%';
--in 子查询
select * from student where id in (1, 2);
--not in 不在其中
select * from student where id not in (1, 2);
--is null 是空
select * from student where age is null;
--is not null 不为空
select * from student where age is not null;
--order by 排序
select * from student order by name;
select * from student order by name desc;
select * from student order by name asc;
--group by 分组
按照年龄进行分组统计
select count(age), age from student group by age;
按照性别进行分组统计
select count(*), sex from student group by sex;
按照年龄和性别组合分组统计,并排序
select count(*), sex from student group by sex, age order by age;
按照性别分组,并且是id大于2的记录最后按照性别排序
select count(*), sex from student where id > 2 group by sex order by sex;
查询id大于2的数据,并完成运算后的结果进行分组和排序
select count(*), (sex * id) new from student where id > 2 group by sex * id order by sex * id;
--group by all 所有分组
按照年龄分组,是所有的年龄
select count(*), age from student group by all age;
--having 分组过滤条件
按照年龄分组,过滤年龄为空的数据,并且统计分组的条数和现实年龄信息
select count(*), age from student group by age having age is not null;
按照年龄和cid组合分组,过滤条件是cid大于1的记录
select count(*), cid, sex from student group by cid, sex having cid > 1;
按照年龄分组,过滤条件是分组后的记录条数大于等于2
select count(*), age from student group by age having count(age) >= 2;
按照cid和性别组合分组,过滤条件是cid大于1,cid的最大值大于2
select count(*), cid, sex from student group by cid, sex having cid > 1 and max(cid) > 2;
Ø 嵌套子查询
子查询是一个嵌套在select、insert、update或delete语句或其他子查询中的查询。任何允许使用表达式的地方都可以使用子查询。子查询也称为内部查询或内部选择,而包含子查询的语句也成为外部查询或外部选择。
# from (select … table)示例
将一个table的查询结果当做一个新表进行查询
select * from (
select id, name from student where sex = 1
) t where t.id > 2;
上面括号中的语句,就是子查询语句(内部查询)。在外面的是外部查询,其中外部查询可以包含以下语句:
1、 包含常规选择列表组件的常规select查询
2、 包含一个或多个表或视图名称的常规from语句
3、 可选的where子句
4、 可选的group by子句
5、 可选的having子句
# 示例
查询班级信息,统计班级学生人生
select *, (select count(*) from student where cid = classes.id) as num
from classes order by num;
# in, not in子句查询示例
查询班级id大于小于的这些班级的学生信息
select * from student where cid in (
select id from classes where id > 2 and id < 4
);
查询不是班的学生信息
select * from student where cid not in (
select id from classes where name = '2班'
)
in、not in 后面的子句返回的结果必须是一列,这一列的结果将会作为查询条件对应前面的条件。如cid对应子句的id;
# exists和not exists子句查询示例
查询存在班级id为的学生信息
select * from student where exists (
select * from classes where id = student.cid and id = 3
);
查询没有分配班级的学生信息
select * from student where not exists (
select * from classes where id = student.cid
);
exists和not exists查询需要内部查询和外部查询进行一个关联的条件,如果没有这个条件将是查询到的所有信息。如:id等于student.id;
# some、any、all子句查询示例
查询班级的学生年龄大于班级的学生的年龄的信息
select * from student where cid = 5 and age > all (
select age from student where cid = 3
);
select * from student where cid = 5 and age > any (
select age from student where cid = 3
);
select * from student where cid = 5 and age > some (
select age from student where cid = 3
);
Ø 聚合查询
1、 distinct去掉重复数据
select distinct sex from student;
select count(sex), count(distinct sex) from student;
2、 compute和compute by汇总查询
对年龄大于的进行汇总
select age from student
where age > 20 order by age compute sum(age) by age;
对年龄大于的按照性别进行分组汇总年龄信息
select id, sex, age from student
where age > 20 order by sex, age compute sum(age) by sex;
按照年龄分组汇总
select age from student
where age > 20 order by age, id compute sum(age);
按照年龄分组,年龄汇总,id找最大值
select id, age from student
where age > 20 order by age compute sum(age), max(id);
compute进行汇总前面是查询的结果,后面一条结果集就是汇总的信息。compute子句中可以添加多个汇总表达式,可以添加的信息如下:
a、 可选by关键字。它是每一列计算指定的行聚合
b、 行聚合函数名称。包括sum、avg、min、max、count等
c、 要对其执行聚合函数的列
compute by适合做先分组后汇总的业务。compute by后面的列一定要是order by中出现的列。
3、 cube汇总
cube汇总和compute效果类似,但语法较简洁,而且返回的是一个结果集。
select count(*), sex from student group by sex with cube;
select count(*), age, sum(age) from student where age is not null group by age with cube;
cube要结合group by语句完成分组汇总
Ø 排序函数
排序在很多地方需要用到,需要对查询结果进行排序并且给出序号。比如:
1、 对某张表进行排序,序号需要递增不重复的
2、 对学生的成绩进行排序,得出名次,名次可以并列,但名次的序号是连续递增的
3、 在某些排序的情况下,需要跳空序号,虽然是并列
基本语法
排序函数 over([分组语句] 排序子句[desc][asc])
排序子句 order by 列名, 列名
分组子句 partition by 分组列, 分组列
# row_number函数
根据排序子句给出递增连续序号
按照名称排序的顺序递增
select s.id, s.name, cid, c.name, row_number() over(order by c.name) as number
from student s, classes c where cid = c.id;
# rank函数函数
根据排序子句给出递增的序号,但是存在并列并且跳空
顺序递增
select id, name, rank() over(order by cid) as rank from student;
跳过相同递增
select s.id, s.name, cid, c.name, rank() over(order by c.name) as rank
from student s, classes c where cid = c.id;
# dense_rank函数
根据排序子句给出递增的序号,但是存在并列不跳空
不跳过,直接递增
select s.id, s.name, cid, c.name, dense_rank() over(order by c.name) as dense
from student s, classes c where cid = c.id;
# partition by分组子句
可以完成对分组的数据进行增加排序,partition by可以与以上三个函数联合使用。
利用partition by按照班级名称分组,学生id排序
select s.id, s.name, cid, c.name, row_number() over(partition by c.name order by s.id) as rank
from student s, classes c where cid = c.id;
select s.id, s.name, cid, c.name, rank() over(partition by c.name order by s.id) as rank
from student s, classes c where cid = c.id;
select s.id, s.name, cid, c.name, dense_rank() over(partition by c.name order by s.id) as rank
from student s, classes c where cid = c.id;
# ntile平均排序函数
将要排序的数据进行平分,然后按照等分排序。ntile中的参数代表分成多少等分。
select s.id, s.name, cid, c.name,
ntile(5) over(order by c.name) as ntile
from student s, classes c where cid = c.id;
Ø 集合运算
操作两组查询结果,进行交集、并集、减集运算
1、 union和union all进行并集运算
--union 并集、不重复
select id, name from student where name like 'ja%'
union
select id, name from student where id = 4;
--并集、重复
select * from student where name like 'ja%'
union all
select * from student;
2、 intersect进行交集运算
--交集(相同部分)
select * from student where name like 'ja%'
intersect
select * from student;
3、 except进行减集运算
--减集(除相同部分)
select * from student where name like 'ja%'
except
select * from student where name like 'jas%';
Ø 公式表表达式
查询表的时候,有时候中间表需要重复使用,这些子查询被重复查询调用,不但效率低,而且可读性低,不利于理解。那么公式表表达式可以解决这个问题。
我们可以将公式表表达式(CET)视为临时结果集,在select、insert、update、delete或是create view语句的执行范围内进行定义。
--表达式
with statNum(id, num) as
(
select cid, count(*)
from student
where id > 0
group by cid
)
select id, num from statNum order by id;
with statNum(id, num) as
(
select cid, count(*)
from student
where id > 0
group by cid
)
select max(id), avg(num) from statNum;
Ø 连接查询
1、 简化连接查询
--简化联接查询
select s.id, s.name, c.id, c.name from student s, classes c where s.cid = c.id;
2、 left join左连接
--左连接
select s.id, s.name, c.id, c.name from student s left join classes c on s.cid = c.id;
3、 right join右连接
--右连接
select s.id, s.name, c.id, c.name from student s right join classes c on s.cid = c.id;
4、 inner join内连接
--内连接
select s.id, s.name, c.id, c.name from student s inner join classes c on s.cid = c.id;
--inner可以省略
select s.id, s.name, c.id, c.name from student s join classes c on s.cid = c.id;
5、 cross join交叉连接
--交叉联接查询,结果是一个笛卡儿乘积
select s.id, s.name, c.id, c.name from student s cross join classes c
--where s.cid = c.id;
6、 自连接(同一张表进行连接查询)
--自连接
select distinct s.* from student s, student s1 where s.id <> s1.id and s.sex = s1.sex;
Ø 函数
1、 聚合函数
max最大值、min最小值、count统计、avg平均值、sum求和、var求方差
select
max(age) max_age,
min(age) min_age,
count(age) count_age,
avg(age) avg_age,
sum(age) sum_age,
var(age) var_age
from student;
2、 日期时间函数
select dateAdd(day, 3, getDate());--加天
select dateAdd(year, 3, getDate());--加年
select dateAdd(hour, 3, getDate());--加小时
--返回跨两个指定日期的日期边界数和时间边界数
select dateDiff(day, '2011-06-20', getDate());
--相差秒数
select dateDiff(second, '2011-06-22 11:00:00', getDate());
--相差小时数
select dateDiff(hour, '2011-06-22 10:00:00', getDate());
select dateName(month, getDate());--当前月份
select dateName(minute, getDate());--当前分钟
select dateName(weekday, getDate());--当前星期
select datePart(month, getDate());--当前月份
select datePart(weekday, getDate());--当前星期
select datePart(second, getDate());--当前秒数
select day(getDate());--返回当前日期天数
select day('2011-06-30');--返回当前日期天数
select month(getDate());--返回当前日期月份
select month('2011-11-10');
select year(getDate());--返回当前日期年份
select year('2010-11-10');
select getDate();--当前系统日期
select getUTCDate();--utc日期
3、 数学函数
select pi();--PI函数
select rand(100), rand(50), rand(), rand();--随机数
select round(rand(), 3), round(rand(100), 5);--精确小数位
--精确位数,负数表示小数点前
select round(123.456, 2), round(254.124, -2);
select round(123.4567, 1, 2);
4、 元数据
select col_name(object_id('student'), 1);--返回列名
select col_name(object_id('student'), 2);
--该列数据类型长度
select col_length('student', col_name(object_id('student'), 2));
--该列数据类型长度
select col_length('student', col_name(object_id('student'), 1));
--返回类型名称、类型id
select type_name(type_id('varchar')), type_id('varchar');
--返回列类型长度
select columnProperty(object_id('student'), 'name', 'PRECISION');
--返回列所在索引位置
select columnProperty(object_id('student'), 'sex', 'ColumnId');
5、 字符串函数
select ascii('a');--字符转换ascii值
select ascii('A');
select char(97);--ascii值转换字符
select char(65);
select nchar(65);
select nchar(45231);
select nchar(32993);--unicode转换字符
select unicode('A'), unicode('中');--返回unicode编码值
select soundex('hello'), soundex('world'), soundex('word');
select patindex('%a', 'ta'), patindex('%ac%', 'jack'), patindex('dex%', 'dexjack');--匹配字符索引
select 'a' + space(2) + 'b', 'c' + space(5) + 'd';--输出空格
select charIndex('o', 'hello world');--查找索引
select charIndex('o', 'hello world', 6);--查找索引
select quoteName('abc[]def'), quoteName('123]45');
--精确数字
select str(123.456, 2), str(123.456, 3), str(123.456, 4);
select str(123.456, 9, 2), str(123.456, 9, 3), str(123.456, 6, 1), str(123.456, 9, 6);
select difference('hello', 'helloWorld');--比较字符串相同
select difference('hello', 'world');
select difference('hello', 'llo');
select difference('hello', 'hel');
select difference('hello', 'hello');
select replace('abcedef', 'e', 'E');--替换字符串
select stuff('hello world', 3, 4, 'ABC');--指定位置替换字符串
select replicate('abc#', 3);--重复字符串
select subString('abc', 1, 1), subString('abc', 1, 2), subString('hello Wrold', 7, 5);--截取字符串
select len('abc');--返回长度
select reverse('sqlServer');--反转字符串
select left('leftString', 4);--取左边字符串
select left('leftString', 7);
select right('leftString', 6);--取右边字符串
select right('leftString', 3);
select lower('aBc'), lower('ABC');--小写
select upper('aBc'), upper('abc');--大写
--去掉左边空格
select ltrim(' abc'), ltrim('# abc#'), ltrim(' abc');
--去掉右边空格
select rtrim(' abc '), rtrim('# abc# '), rtrim('abc');
6、 安全函数
select current_user;
select user;
select user_id(), user_id('dbo'), user_id('public'), user_id('guest');
select user_name(), user_name(1), user_name(0), user_name(2);
select session_user;
select suser_id('sa');
select suser_sid(), suser_sid('sa'), suser_sid('sysadmin'), suser_sid('serveradmin');
select is_member('dbo'), is_member('public');
select suser_name(), suser_name(1), suser_name(2), suser_name(3);
select suser_sname(), suser_sname(0x01), suser_sname(0x02), suser_sname(0x03);
select is_srvRoleMember('sysadmin'), is_srvRoleMember('serveradmin');
select permissions(object_id('student'));
select system_user;
select schema_id(), schema_id('dbo'), schema_id('guest');
select schema_name(), schema_name(1), schema_name(2), schema_name(3);
7、 系统函数
select app_name();--当前会话的应用程序名称
select cast(2011 as datetime), cast('10' as money), cast('0' as varbinary);--类型转换
select convert(datetime, '2011');--类型转换
select coalesce(null, 'a'), coalesce('123', 'a');--返回其参数中第一个非空表达式
select collationProperty('Traditional_Spanish_CS_AS_KS_WS', 'CodePage');
select current_timestamp;--当前时间戳
select current_user;
select isDate(getDate()), isDate('abc'), isNumeric(1), isNumeric('a');
select dataLength('abc');
select host_id();
select host_name();
select db_name();
select ident_current('student'), ident_current('classes');--返回主键id的最大值
select ident_incr('student'), ident_incr('classes');--id的增量值
select ident_seed('student'), ident_seed('classes');
select @@identity;--最后一次自增的值
select identity(int, 1, 1) as id into tab from student;--将studeng表的烈属,以/1自增形式创建一个tab
select * from tab;
select @@rowcount;--影响行数
select @@cursor_rows;--返回连接上打开的游标的当前限定行的数目
select @@error;--T-SQL的错误号
select @@procid;
8、 配置函数
set datefirst 7;--设置每周的第一天,表示周日
select @@datefirst as '星期的第一天', datepart(dw, getDate()) AS '今天是星期';
select @@dbts;--返回当前数据库唯一时间戳
set language 'Italian';
select @@langId as 'Language ID';--返回语言id
select @@language as 'Language Name';--返回当前语言名称
select @@lock_timeout;--返回当前会话的当前锁定超时设置(毫秒)
select @@max_connections;--返回SQL Server 实例允许同时进行的最大用户连接数
select @@MAX_PRECISION AS 'Max Precision';--返回decimal 和numeric 数据类型所用的精度级别
select @@SERVERNAME;--SQL Server 的本地服务器的名称
select @@SERVICENAME;--服务名
select @@SPID;--当前会话进程id
select @@textSize;
select @@version;--当前数据库版本信息
9、 系统统计函数
select @@CONNECTIONS;--连接数
select @@PACK_RECEIVED;
select @@CPU_BUSY;
select @@PACK_SENT;
select @@TIMETICKS;
select @@IDLE;
select @@TOTAL_ERRORS;
select @@IO_BUSY;
select @@TOTAL_READ;--读取磁盘次数
select @@PACKET_ERRORS;--发生的网络数据包错误数
select @@TOTAL_WRITE;--sqlserver执行的磁盘写入次数
select patIndex('%soft%', 'microsoft SqlServer');
select patIndex('soft%', 'software SqlServer');
select patIndex('%soft', 'SqlServer microsoft');
select patIndex('%so_gr%', 'Jsonisprogram');
10、 用户自定义函数
# 查看当前数据库所有函数
--查询所有已创建函数
select definition,* from sys.sql_modules m join sys.objects o on m.object_id = o.object_id
and type in('fn', 'if', 'tf');
# 创建函数
if (object_id('fun_add', 'fn') is not null)
drop function fun_add
go
create function fun_add(@num1 int, @num2 int)
returns int
with execute as caller
as
begin
declare @result int;
if (@num1 is null)
set @num1 = 0;
if (@num2 is null)
set @num2 = 0;
set @result = @num1 + @num2;
return @result;
end
go
调用函数
select dbo.fun_add(id, age) from student;
--自定义函数,字符串连接
if (object_id('fun_append', 'fn') is not null)
drop function fun_append
go
create function fun_append(@args nvarchar(1024), @args2 nvarchar(1024))
returns nvarchar(2048)
as
begin
return @args + @args2;
end
go
select dbo.fun_append(name, 'abc') from student;
# 修改函数
alter function fun_append(@args nvarchar(1024), @args2 nvarchar(1024))
returns nvarchar(1024)
as
begin
declare @result varchar(1024);
--coalesce返回第一个不为null的值
set @args = coalesce(@args, '');
set @args2 = coalesce(@args2, '');
set @result = @args + @args2;
return @result;
end
go
select dbo.fun_append(name, '#abc') from student;
# 返回table类型函数
--返回table对象函数
select name, object_id, type from sys.objects where type in ('fn', 'if', 'tf') or type like '%f%';
if (exists (select * from sys.objects where type in ('fn', 'if', 'tf') and name = 'fun_find_stuRecord'))
drop function fun_find_stuRecord
go
create function fun_find_stuRecord(@id int)
returns table
as
return (select * from student where id = @id);
go
select * from dbo.fun_find_stuRecord(2);
SQL Server中的加密
简介
加密是指通过使用密钥或密码对数据进行模糊处理的过程。在SQL Server中,加密并不能替代其他的安全设置,比如防止未被授权的人访问数据库或是数据库实例所在的Windows系统,甚至是数据库所在的机房,而是作为当数据库被破解或是备份被窃取后的最后一道防线。通过加密,使得未被授权的人在没有密钥或密码的情况下所窃取的数据变得毫无意义。这种做法不仅仅是为了你的数据安全,有时甚至是法律所要求的(像国内某知名IT网站泄漏密码这种事在中国可以道歉后不负任何责任了事,在米国妥妥的要破产清算)。
SQL Server中的加密简介
在SQL Server2000和以前的版本,是不支持加密的。所有的加密操作都需要在程序中完成。这导致一个问题,数据库中加密的数据仅仅是对某一特定程序有意义,而另外的程序如果没有对应的解密算法,则数据变得毫无意义。
到了SQL Server2005,引入了列级加密。使得加密可以对特定列执行,这个过程涉及4对加密和解密的内置函数
SQL Server 2008时代,则引入的了透明数据加密(TDE),所谓的透明数据加密,就是加密在数据库中进行,但从程序的角度来看就好像没有加密一样,和列级加密不同的是,TDE加密的级别是整个数据库。使用TDE加密的数据库文件或备份在另一个没有证书的实例上是不能附加或恢复的。 Continue reading “SQL Server中的加密”
SQL Server死锁总结
原文出处 http://www.cnblogs.com/happyhippy/archive/2008/11/14/1333922.html
- 死锁原理
根据操作系统中的定义:死锁是指在一组进程中的各个进程均占有不会释放的资源,但因互相申请被其他进程所站用不会释放的资源而处于的一种永久等待状态。死锁的四个必要条件:
互斥条件(Mutual exclusion):资源不能被共享,只能由一个进程使用。
请求与保持条件(Hold and wait):已经得到资源的进程可以再次申请新的资源。
非剥夺条件(No pre-emption):已经分配的资源不能从相应的进程中被强制地剥夺。
循环等待条件(Circular wait):系统中若干进程组成环路,该环路中每个进程都在等待相邻进程正占用的资源。对应到SQL Server中,当在两个或多个任务中,如果每个任务锁定了其他任务试图锁定的资源,此时会造成这些任务永久阻塞,从而出现死锁;这些资源可能是:单行(RID,堆中的单行)、索引中的键(KEY,行锁)、页(PAG,8KB)、区结构(EXT,连续的8页)、堆或B树(HOBT) 、表(TAB,包括数据和索引)、文件(File,数据库文件)、应用程序专用资源(APP)、元数据(METADATA)、分配单元(Allocation_Unit)、整个数据库(DB)。一个死锁示例如下图所示:
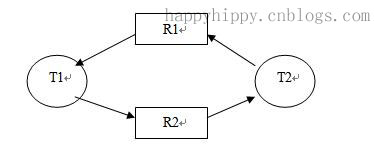
说明:T1、T2表示两个任务;R1和R2表示两个资源;由资源指向任务的箭头(如R1->T1,R2->T2)表示该资源被改任务所持有;由任务指向资源的箭头(如T1->S2,T2->S1)表示该任务正在请求对应目标资源;
其满足上面死锁的四个必要条件:
(1).互斥:资源S1和S2不能被共享,同一时间只能由一个任务使用;
(2).请求与保持条件:T1持有S1的同时,请求S2;T2持有S2的同时请求S1;
(3).非剥夺条件:T1无法从T2上剥夺S2,T2也无法从T1上剥夺S1;
(4).循环等待条件:上图中的箭头构成环路,存在循环等待。
sql server 分区表
IF EXISTS(
SELECT 1
FROM sys.databases AS d
WHERE d.name = 'Test_1'
)
DROP DATABASE Test_1
GO
CREATE DATABASE [Test_1] ON PRIMARY(
NAME
=
N'Test_1',
FILENAME
=
N'E:\Database\Sharding\Test_1.mdf',
SIZE
=
10240KB,
MAXSIZE
=
UNLIMITED,
FILEGROWTH
=
1024Kb
),
FILEGROUP [Test_A](
NAME = N'Test_A',
FILENAME = 'E:\Database\Sharding\Test_A.ndf',
SIZE = 10240kb,
MAXSIZE = UNLIMITED,
FILEGROWTH = 1024kB
),
FILEGROUP [Test_B](
NAME = N'Test_B',
FILENAME = 'E:\Database\Sharding\Test_B.ndf',
SIZE = 10240kb,
MAXSIZE = UNLIMITED,
FILEGROWTH = 1024kB
)
LOG ON (
NAME = N'Test_log',
FILENAME = 'E:\Database\Sharding\Test_Log.ldf',
SIZE = 10240kb,
MAXSIZE = UNLIMITED,
FILEGROWTH = 1024kB
) COLLATE Chinese_PRC_CI_AS
GO
USE [Test_1]
IF EXISTS(
SELECT 1
FROM sys.partition_functions AS pf
WHERE pf.name = 'TEST_PART'
)
DROP PARTITION FUNCTION [TEST_PART]
GO
-- set a partiton condition
CREATE PARTITION FUNCTION TEST_PART(INT) AS RANGE LEFT FOR VALUES(2)
GO
IF EXISTS(
SELECT 1
FROM sys.partition_schemes AS ps
WHERE ps.name = 'TEST_SCH'
)
DROP PARTITION SCHEME [TEST_SCH]
GO
--set a scheme for table using.
CREATE PARTITION SCHEME TEST_SCH
AS PARTITION [TEST_PART] TO (Test_A, Test_B)
GO
IF OBJECT_ID('STUDENT', 'U') IS NOT NULL
DROP TABLE STUDENT
GO
CREATE TABLE STUDENT
(
Id INT IDENTITY(1, 1) NOT NULL,
NAME VARCHAR(10) NULL,
CLASS INT NULL,
GRADE INT NULL
) ON TEST_SCH(Id) -- set scheme
GO
INSERT INTO STUDENT
(
-- Id -- this column value is auto-generated
NAME,
CLASS,
GRADE
)
VALUES
(
'A',
1,
1
);
INSERT INTO STUDENT
(
-- Id -- this column value is auto-generated
NAME,
CLASS,
GRADE
)
VALUES
(
'B',
2,
2
);
INSERT INTO STUDENT
(
-- Id -- this column value is auto-generated
NAME,
CLASS,
GRADE
)
VALUES
(
'C',
3,
3
);
INSERT INTO STUDENT
(
-- Id -- this column value is auto-generated
NAME,
CLASS,
GRADE
)
VALUES
(
'D',
4,
4
)
GO
SQL Server调优系列进阶篇(如何维护数据库索引)
技术准备
数据库版本为SQL Server2012,前几篇文章用的是SQL Server2008RT,内容区别不大,利用微软的以前的案例库(Northwind)进行分析,部分内容也会应用微软的另一个案例库AdventureWorks。
相信了解SQL Server的朋友,对这两个库都不会太陌生。
一、创建索引
当我们要开始对表进行索引的创建的时候,首先明确的是,一张表内只能创建一个聚集索引,最多可以创建最多249个非聚集索引(SQL Server2005),在SQL Server2008以后聚集索引数提升至999个,上一篇文章我们知道对于聚集索引项一般要创建上,而非聚集索引项要根据日常的T-SQL语句进行选择。
关于索引的选择是一个很考验调优能力的事情,大部分的情况下优质的索引新建全靠经验而论,有兴趣的可以点击查阅我前面的一系列关于分析查询计划的文章,掌握住里面的精髓才能有的放矢。
当然,小白级别的也可以参照如下方法尝试进行创建:
由于SQL Server有着自己的一套调优技巧,所以在我们每次运行的T-SQL语句应该怎样优化,SQL Server是了如指掌的,所以它会将缺失的索引项进行记录,用于提示使用者,尝试去建立这些索引。
主要记录在以下几个DMV中
sys.dm_db_missing_index_details sys.dm_db_missing_index_groups sys.dm_db_missing_index_group_stats sys.dm_db_missing_index_columns(index_handle) sys.dm_db_missing_index_details
SQL Server调优系列进阶篇(如何索引调优)
前言
上一篇我们分析了数据库中的统计信息的作用,我们已经了解了数据库如何通过统计信息来掌控数据库中各个表的内容分布。不清楚的童鞋可以点击参考。
作为调优系列的文章,数据库的索引肯定是不能少的了,所以本篇我们就开始分析这块内容,关于索引的基础知识就不打算深入分析了,网上一搜一片片的,本篇更侧重的是一些实战项内容展示,希望通过本篇文章各位看官能在真正的场景中找到合适的解决方法足以。
对于索引的使用,我希望的是遇到问题找到合适的解决方法就可以,切勿乱用!!!
本篇在分析出索引的优越性的同时也将负面影响展现出来。
技术准备
数据库版本为SQL Server2012,前几篇文章用的是SQL Server2008RT,内容区别不大,利用微软的以前的案例库(Northwind)进行分析,部分内容也会应用微软的另一个案例库AdventureWorks
相信了解SQL Server的朋友,对这两个库都不会太陌生。
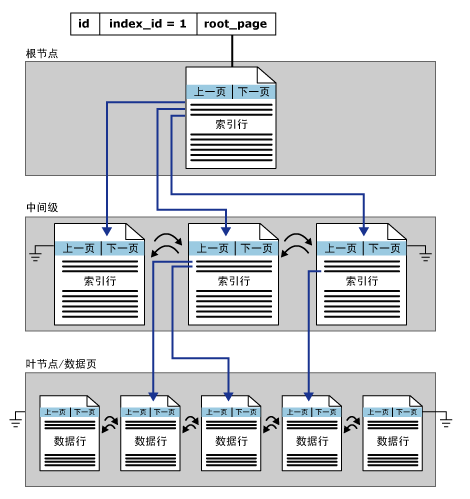
概念理解
所谓的索引同SQL Server中的其它类型的数据页一样,也是固定的8KB(8192字节),存储方式同为B-Tree结构,索引B树中的每一页称为一个索引节点。B树顶端节点为根节点。索引中的底层节点称为叶节点。根节点与叶节点之间的任何索引统称为中间级。
算了,描述起来太麻烦,联机丛书上截个图直观的展示结构:
SQL Server调优系列进阶篇(深入剖析统计信息)
前言
经过前几篇的分析,其实大体已经初窥到SQL Server统计信息的重要性了,所以本篇就要祭出这个神器了。
该篇内容会很长,坐好板凳,瓜子零食之类…
不废话,进正题
技术准备
数据库版本为SQL Server2008R2,利用微软的以前的案例库(Northwind)进行分析,部分内容也会应用微软的另一个案例库AdventureWorks
相信了解SQL Server的朋友,对这两个库都不会太陌生。
概念理解
关于SQL Server中的统计信息,在联机丛书中是这样解释的
查询优化的统计信息是一些对象,这些对象包含与值在表或索引视图的一列或多列中的分布有关的统计信息。查询优化器使用这些统计信息来估计查询结果中的基数或行数。通过这些基数估计,查询优化器可以创建高质量的查询计划。例如,查询优化器可以使用基数估计选择索引查找运算符而不是耗费更多资源的索引扫描运算符,从而提高查询性能。
其实关于统计信息的作用通俗点将就是:SQL Server通过统计信息理解库中每张表的数据内容项分布,知道里面数据“长得啥德行,做到心中有数”,这样每次查询语句的时候就可以根据表中的数据分布,基本能定位到要查找数据的内容位置。
比如,我记得我以前有篇文章写过一个相同的查询语句,但是产生了完全不同的查询计划,这里回顾下,基本如下:
SELECT * FROM Person.Contact WHERE FirstName LIKE 'K%' SELECT * FROM Person.Contact WHERE FirstName LIKE 'Y%'
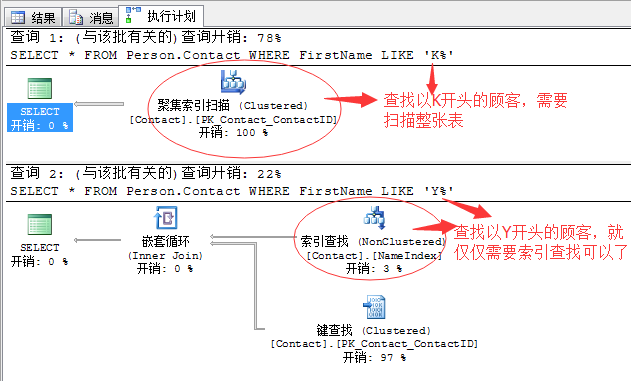
完全相同的查询语句,只是查询条件不同,一个查找以K开头的顾客,一个查找以Y开头的顾客,却产生了完全不同的查询计划。
其实,这里的原因就是统计信息在作祟。 Continue reading “SQL Server调优系列进阶篇(深入剖析统计信息)”
SQL Server调优系列进阶篇(查询语句运行几个指标值监测)
前言
上一篇我们分析了查询优化器的工作方式,其中包括:查询优化器的详细运行步骤、筛选条件分析、索引项优化等信息。
本篇我们分析在我们运行的过程中几个关键指标值的检测。
通过这些指标值来分析语句的运行问题,并且分析其优化方式。
通过本篇我们可以学习到调优中经常利用的几个利器!
废话少说,开始本篇的正题。
技术准备
数据库版本为SQL Server2008R2,利用微软的一个更简洁的案例库(Northwind)进行分析。
利器一、IO统计
通过这个IO统计能为我们分析出当前查询语句所要扫描的数据页的数量。这里面有几个重要的概念,我们依次分析。
方法很简单,一行代码搞定:
SET STATISTICS IO ON
来看个例子
SET STATISTICS IO ON GO SELECT * FROM Person.Contact
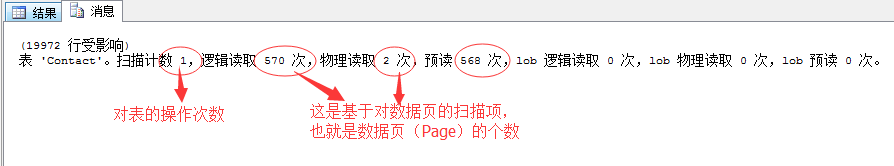
这里可以看到这个语句对于数据表的操作次数,基于数据页的扫描项。 Continue reading “SQL Server调优系列进阶篇(查询语句运行几个指标值监测)”
SQL Server调优系列进阶篇(查询优化器的运行方式)
前言
前面我们的几篇文章介绍了一系列关于运算符的基础介绍,以及各个运算符的优化方式和技巧。其中涵盖:查看执行计划的方式、几种数据集常用的连接方式、联合运算符方式、并行运算符等一系列的我们常见的运算符。有兴趣的童鞋可以点击查看。
本篇介绍在SQL Server中查询优化器的工作方式,也就是一个好的执行计划的形成,是如何评估出来的,作为该系列的进阶篇。
废话少说,开始本篇的正题。
技术准备
数据库版本为SQL Server2008R2,利用微软的一个更简洁的案例库(Northwind)进行分析。
正文内容
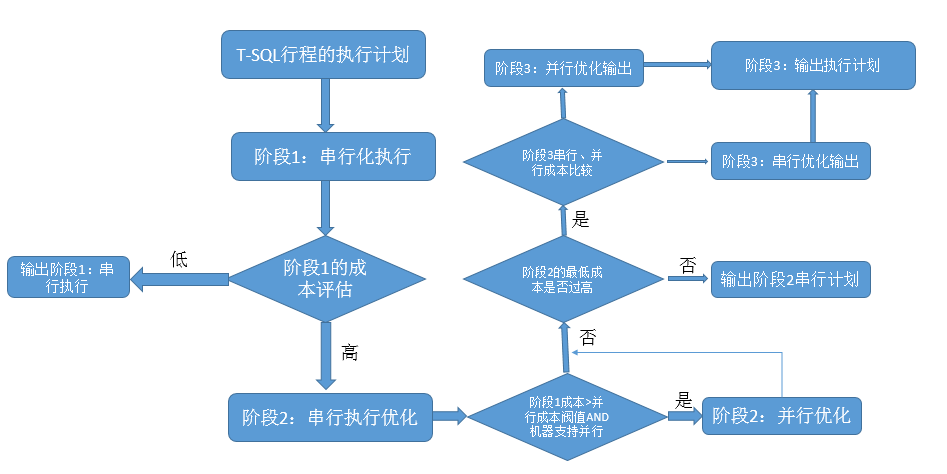
在我们将写好的一个T-SQL语句抛给SQL Server准备执行的时候,首选要经历的过程就是编译过程,当然如果此语句以前在SQL Server中执行过,那么将检测是否存在已经缓存的编译过的执行计划,用以重用。
但是,执行编译的过程需要执行一系列的优化过程,关于优化过程大致分为两个阶段:
1、首先,SQL Server对我们写的T-SQL语句先执行一些简化,通常由查询本身来寻找交互性及重新安排操作的顺序。
在此过程中,SQL Server侧重于语句写法调整,而不过多的考虑成本或者分析索引可用性的等,最重要的目标就是产生一个有效的查询。
然后,SQL Server才会加载元数据,包括索引的统计信息,进入第二个阶段。
2、在这个阶段才是SQL Server一个复杂的优化过程,这个阶段SQL Server会根据上一阶段形成的执行计划运算符进行评估和尝试,甚至于重组执行计划,所以相对这个优化过程是一个耗时的过程。
通过如下流程图,来理解该过程: